IUI - Intra Uterine Insemination
Intra Uterine Insemination (IUI)
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a relatively low tech assisted conception service (fertility treatment). Intrauterine insemination involves preparing the male partners sperm in the laboratory and then placing only those sperm which move well and are normally formed in the women's uterus. The sperm are transferred into the uterus at the time of ovulation. IUI can be performed with the sperm of the male partner or with donor sperm.
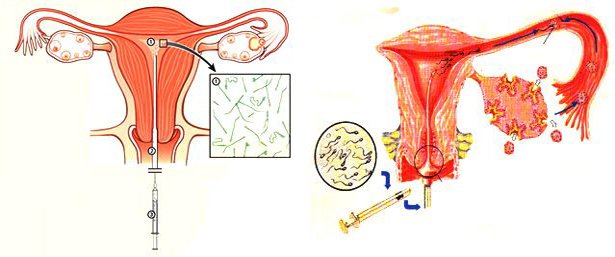
The success of intrauterine insemination depends on 2 factors:
- The indication for intrauterine insemination (the reason it is being performed)
- Whether performed in a drug stimulated or natural (drug free) cycle
In general intrauterine insemination is a good assisted conception treatment if it is performed to overcome a problem of lack of sperm ie using donor sperm for severe male subfertility, and for single women or lesbian couples. It is also successful if intercourse is not occurring normally such as in cases of ejaculation dysfunction (ED). Intrauterine insemination is moderately successful when used for cervical mucus hostility when sperm are killed within the cervix. Intrauterine insemination tends to be less useful if the indication is male factor subfertility ie low numbers or movement of sperm or in unexplained infertility.
Ovulation Induction (OI)
For women who are not ovulating regularly, the goal of treatment is to mature and ovulate a single egg – ovulation induction (OI) as referred to previously. Clomiphene alone often works well to cause the ovaries to mature an egg. A typical protocol will involve taking clomiphene each day for cycle days 3-7 or cycle days 5-9. Ultrasounds and blood tests are then used to monitor the egg as it matures. Once the egg is ready, a subcutaneous injection is given of a hormone called hCG (the ‘trigger shot’), which triggers ovulation of that egg approximately 38-40 hours after the injection.
In women whose irregular ovulation is due to PCOS, a medication called metformin may be added to the treatment regimen. For those women who do not respond to clomiphene, FSH may be added to the protocol. In women who do not ovulate due to hypothalamic amenorrhea, injectible medications containing both FSH and LH are used to stimulate the ovaries to mature an egg. An Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) is commonly performed in the OI cycle.